1. Project Overview
This project implements a production-grade MLOps pipeline for binary image classification (dandelions vs grass) using modern cloud-native technologies. The pipeline covers the entire ML lifecycle: data preprocessing, model training with experiment tracking, containerized deployment, automated retraining, and continuous integration/deployment.
Key Objectives
- End-to-End Automation: Apache Airflow DAGs for automated data extraction, training, and model updates
- Experiment Tracking: MLflow for versioning models, parameters, and metrics with S3 storage
- Cloud-Native Deployment: Kubernetes orchestration with FastAPI serving and Streamlit UI
- CI/CD Pipeline: GitHub Actions for automated testing, Docker builds, and deployment
- Reproducibility: Full containerization with Docker Compose for local development
2. Technology Stack
Modern MLOps stack combining orchestration, ML frameworks, storage, and deployment tools.
- Orchestration: Apache Airflow for workflow automation and scheduling
- ML Framework: PyTorch with EfficientNet (B0-B5) transfer learning
- Experiment Tracking: MLflow for model registry and versioning
- Storage: PostgreSQL (feature store), AWS S3/MinIO (model artifacts)
- Deployment: Kubernetes, Docker, FastAPI, Streamlit, GitHub Actions
3. Data Extraction & Preprocessing
Automated pipeline for downloading, cleaning, and storing image features with data augmentation.
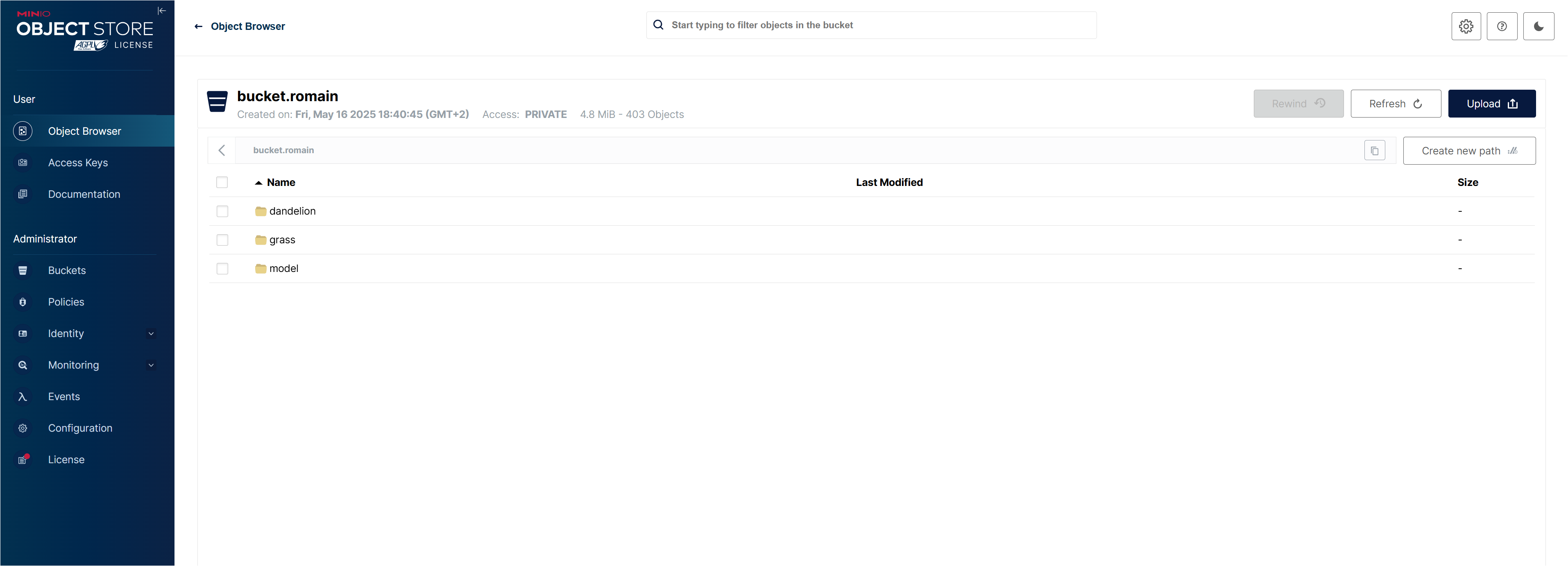
Figure 1 - Automated data extraction and preprocessing pipeline
- Data Ingestion: Automated download from URLs with validation and quality checks
- Augmentation: Flip, rotation, zoom transformations to improve model robustness
- Feature Storage: PostgreSQL feature store with versioning and metadata tracking
4. Model Training & Experiment Tracking
PyTorch-based training with MLflow tracking and S3 model storage.
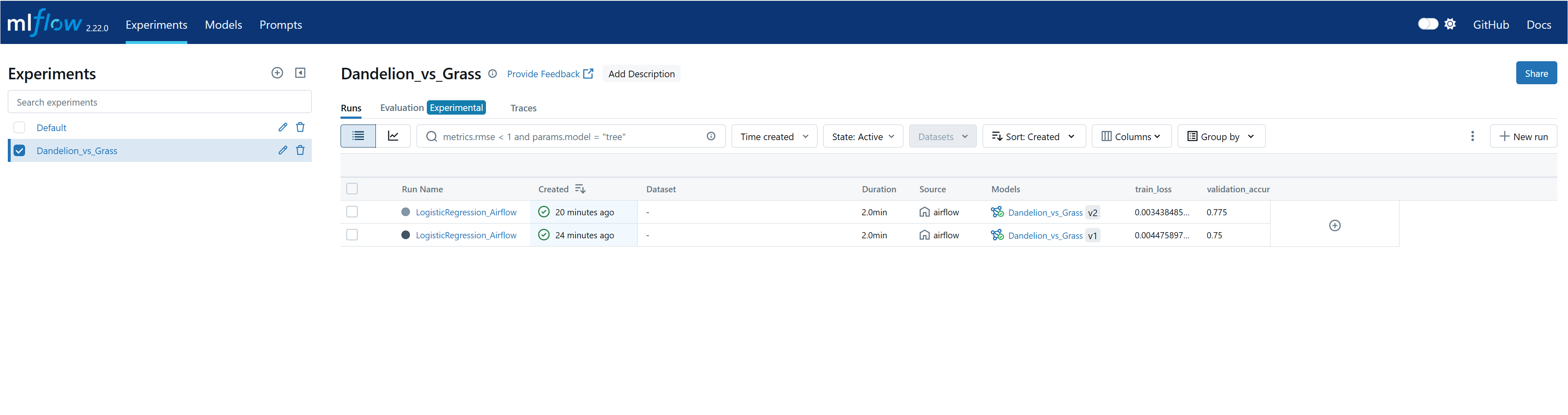
Figure 2 - Model training with MLflow experiment tracking
- Transfer Learning: Pre-trained EfficientNet (B0-B5) fine-tuned on dandelion/grass dataset
- Cross-Validation: Stratified K-Fold for robust evaluation on heterogeneous data
- MLflow Tracking: Automatic logging of parameters, metrics, and model artifacts to S3/MinIO
5. API & Application Deployment
Production deployment with FastAPI backend and Streamlit frontend on Kubernetes.
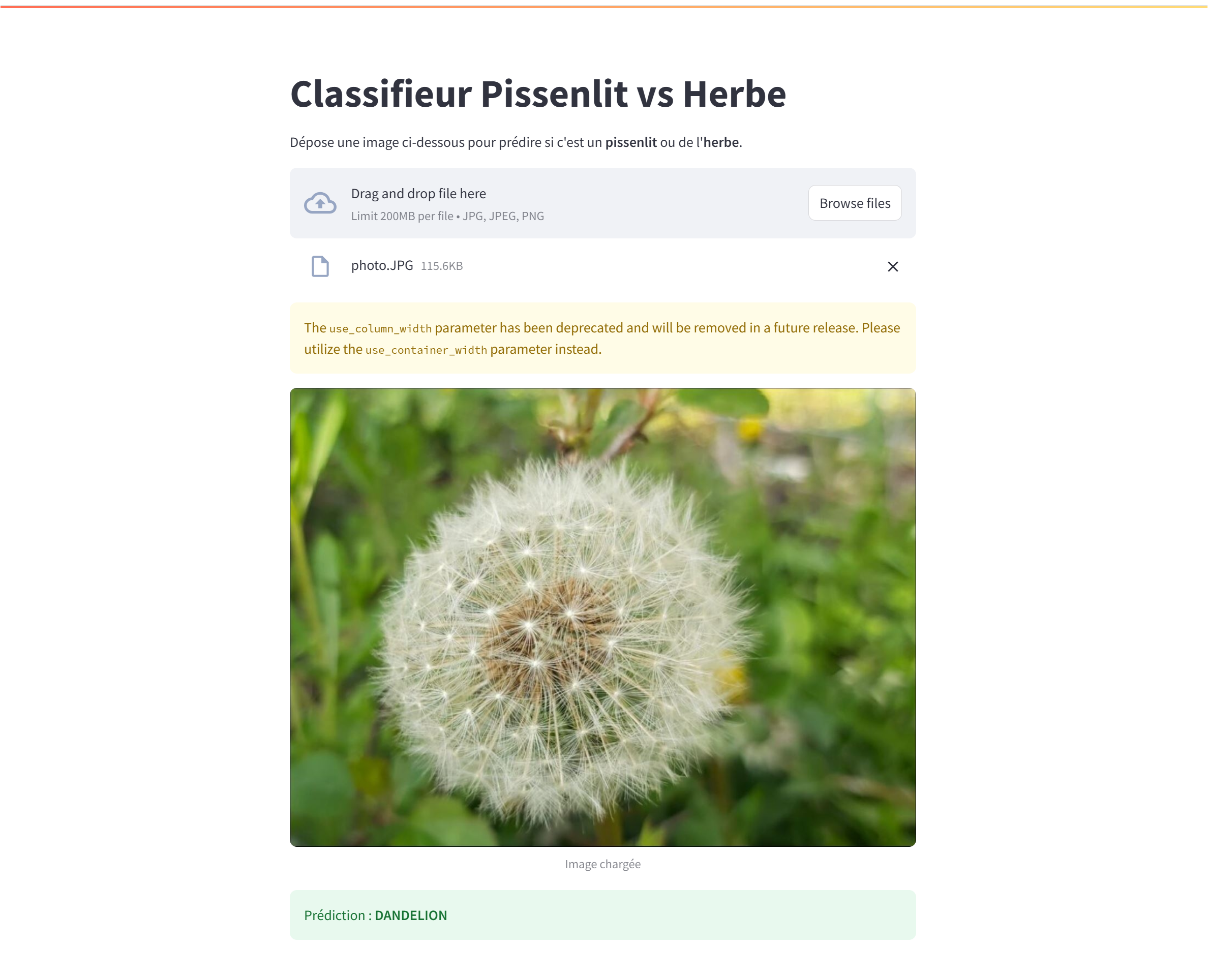
Figure 3 - FastAPI serving and Streamlit web application
- FastAPI: RESTful API for model inference with automatic OpenAPI documentation
- Streamlit UI: Interactive web interface for image upload and classification visualization
- Kubernetes: Scalable deployment with service exposure and resource management
6. Workflow Automation with Apache Airflow
Automated DAGs for periodic retraining and model updates.
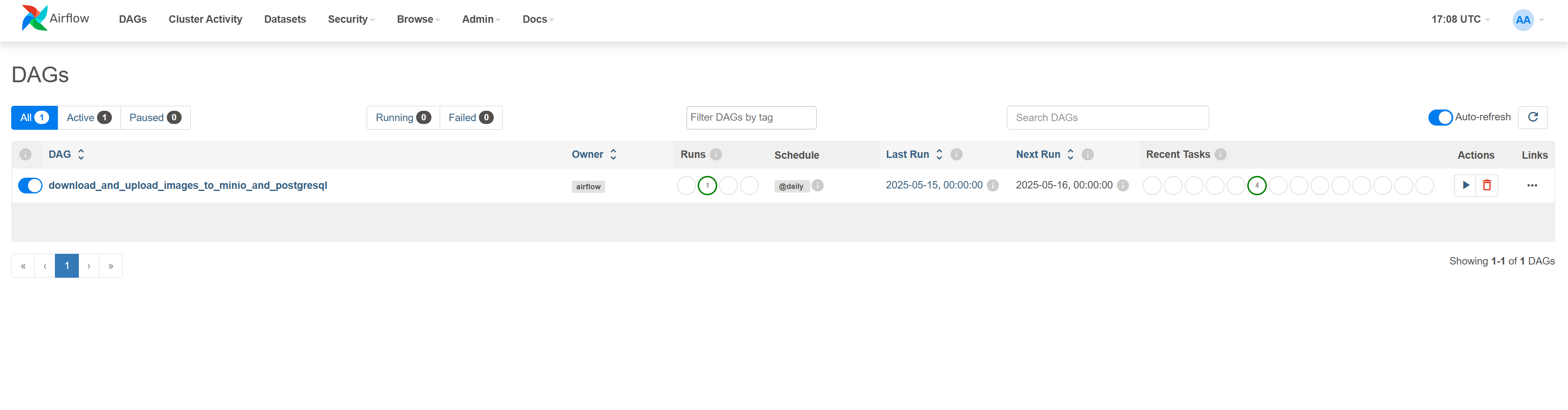
Figure 4 - Airflow DAG for automated training pipeline
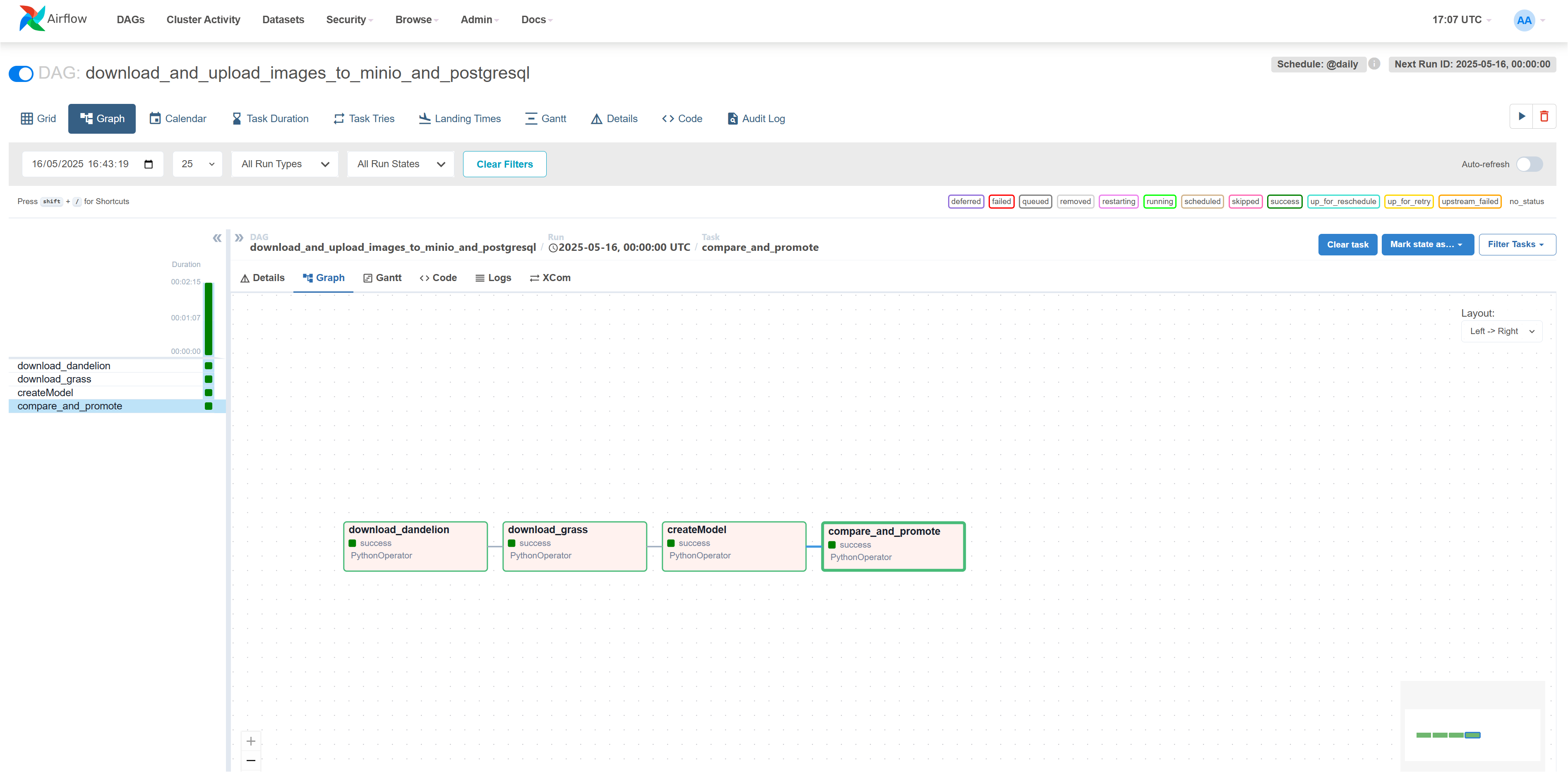
Figure 5 - Airflow task monitoring and execution history
- Scheduled Retraining: Automated DAG triggers for periodic model updates based on new data
- Pipeline Orchestration: End-to-end workflow from data extraction to model deployment
- Monitoring: Real-time task tracking with failure alerts and retry mechanisms
7. CI/CD Pipeline & Testing
GitHub Actions for automated testing, Docker builds, and Kubernetes deployment.
Figure 6 - GitHub Actions CI/CD pipeline with automated tests
- Automated Testing: Unit and integration tests with pytest in CI pipeline
- Docker Build: Containerization with multi-stage builds and DockerHub registry
- Kubernetes Deploy: Automated deployment to local cluster with health checks and rollback
8. Results & Key Takeaways
This project demonstrates a complete MLOps pipeline following industry best practices. The modular architecture enables rapid iteration, while containerization and orchestration ensure reproducibility and scalability. The integration of MLflow, Airflow, and Kubernetes provides enterprise-grade ML operations capabilities.
Future enhancements include cloud deployment (AWS/GCP), model monitoring with Prometheus/Grafana, A/B testing infrastructure, and multi-model serving capabilities.
Technologies & Resources
Key Technologies
- Apache Airflow: Workflow orchestration platform - https://airflow.apache.org/
- MLflow: Open source platform for ML lifecycle - https://mlflow.org/
- PyTorch: Deep learning framework - https://pytorch.org/
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration - https://kubernetes.io/
- FastAPI: Modern API framework - https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/
Project Information
Status: Production-ready, fully deployable locally and on cloud
Deployment: Docker Compose (local) + Kubernetes (Docker Desktop)
Contact: For repository access or technical inquiries, contact Martin LE CORRE
Documentation: 📄 View detailed README