Démonstration complète du système RAG avec ingestion, retrieval hybride, et comparaison Local/Cloud | Début interface user @1min37
Bureau Veritas NR467 (Technical, Guidelines, Notations),
Code du travail (French law),
STBi Report (Scientific technical report)
1. Context and Objectives
In the era of Large Language Models (LLMs), organizations face a critical challenge: leveraging AI capabilities while maintaining data sovereignty and confidentiality. This project addresses this need by developing an advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that can operate entirely on-premise or integrate with cloud providers based on security requirements.
Key Objectives
- Privacy-First Architecture: Enable 100% local deployment for confidential data processing without cloud dependencies
- Hybrid Retrieval: Combine dense vector search, sparse BM25, and advanced fusion techniques for optimal accuracy
- Multi-Cloud Flexibility: Support real-time comparison between local LLMs (Ollama) and cloud providers (Claude, GPT-4, Gemini, Mistral, Cohere)
- Production-Ready Pipeline: Automated document ingestion with intelligent chunking, quality filtering, and metadata enrichment
- Performance Optimization: GPU-accelerated embeddings and efficient indexing for low-latency retrieval
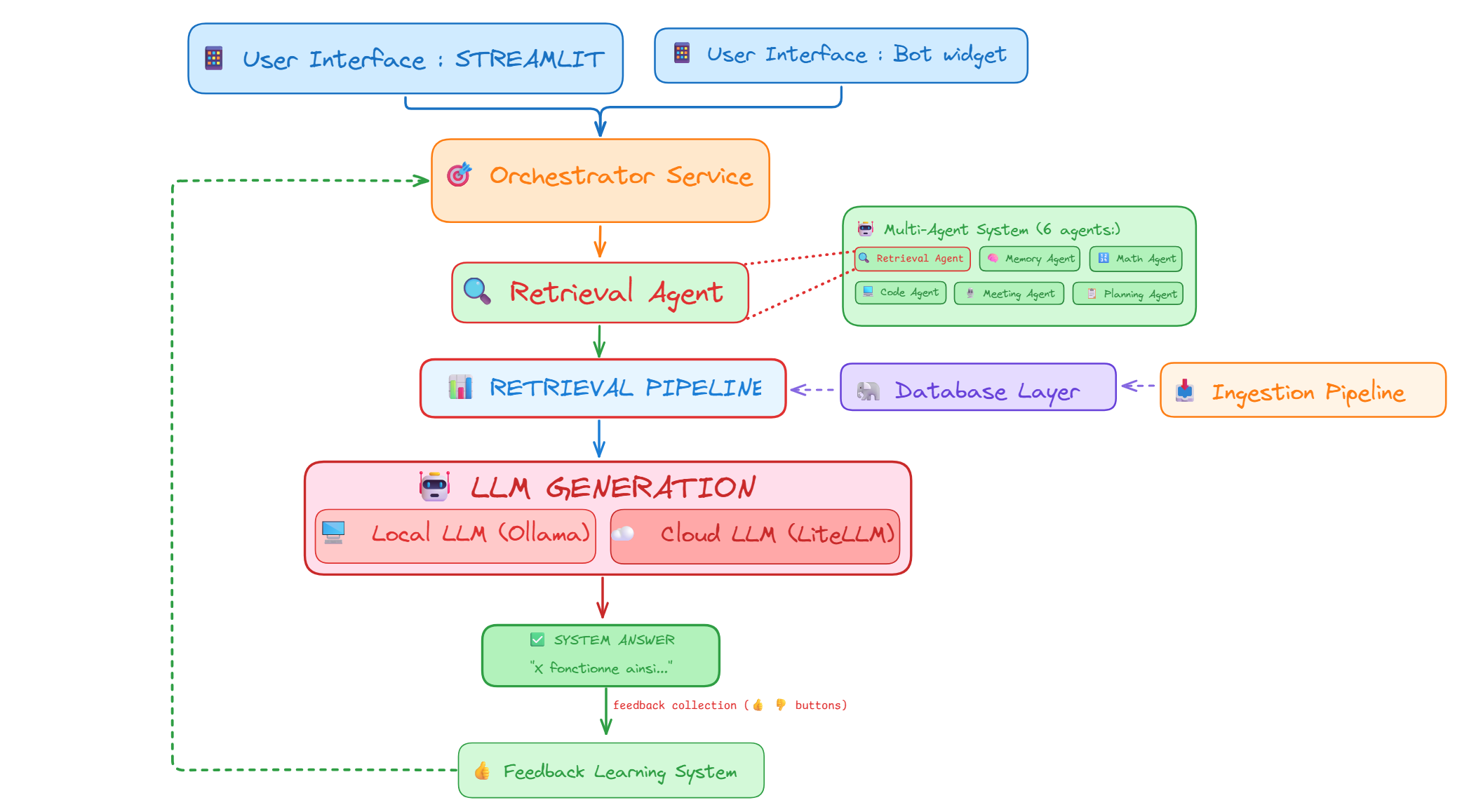
Figure 1 - High-level architecture of the RAG system
The main challenge was to design a system that balances performance, cost, and privacy while maintaining production-grade reliability and scalability.
2. Hybrid Retrieval Architecture
The retrieval system combines dense vector search (mxbai-embed-large), sparse BM25, and Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) to achieve optimal accuracy across diverse query types.
- Dense Search: Semantic embeddings mxbai-embed-large (1024-dim) with PostgreSQL PGVector and HNSW indexing (m=32, ef_construction=128)
- Sparse Search: BM25 keyword matching for exact terminology retrieval
- RRF Fusion: SQL-native algorithm combining results (60% dense + 40% sparse)
- Reranking: Optional CrossEncoder (BAAI/bge-reranker-v2-m3) for 5-10% precision improvement
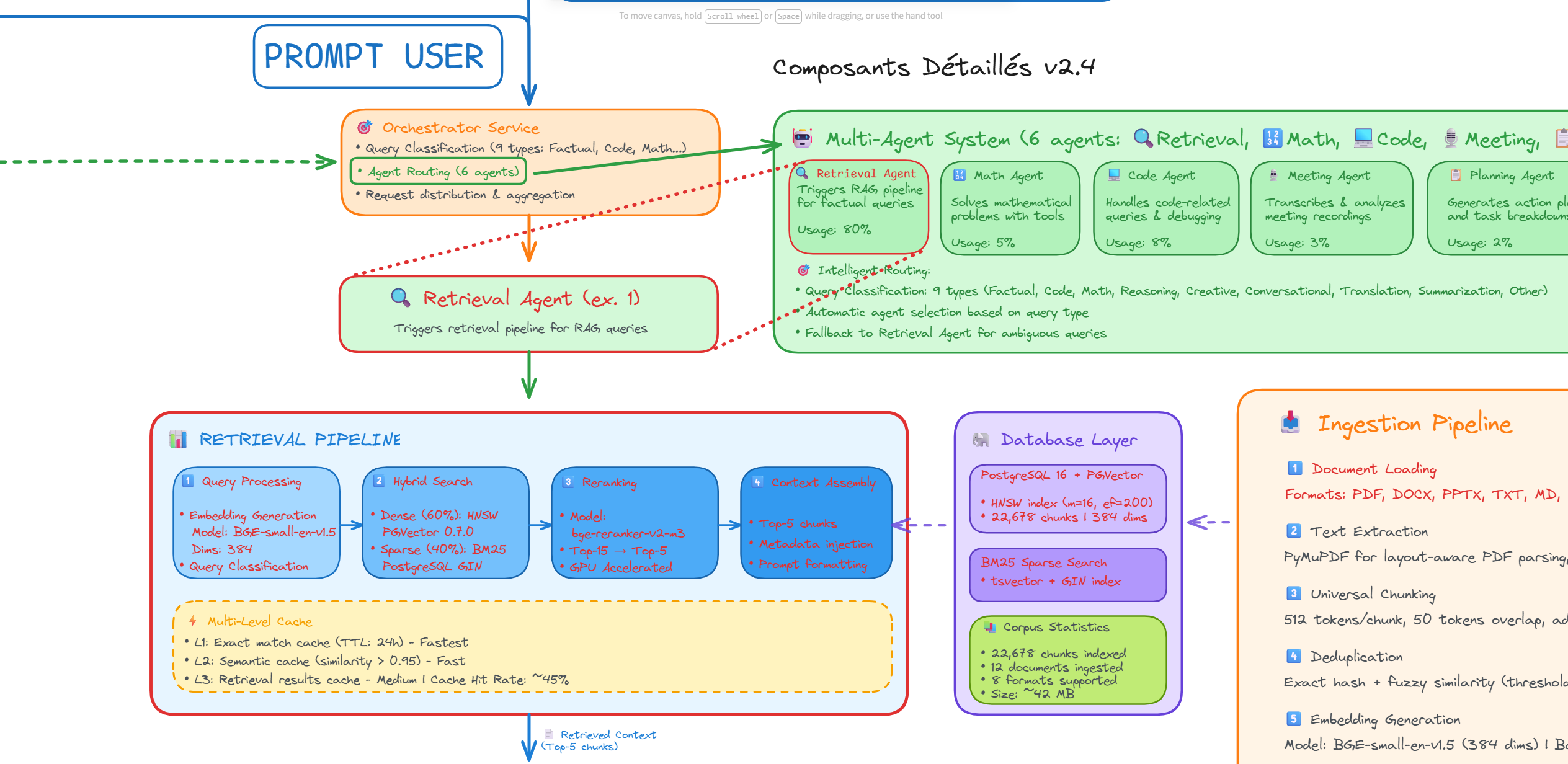
Figure 2 - Hybrid retrieval pipeline combining dense, sparse, and fusion techniques
Advanced Features
- Multi-Agent System: 5 specialized agents (Retrieval, Code, Math, Planning, Memory) with ReAct orchestration for complex tasks
- Meeting Transcription: Automated audio transcription and LLM-powered analysis system
3. LLM Orchestration: Local vs Cloud
The system provides flexible LLM integration with real-time benchmarking capabilities.
- Local Deployment: Ollama with llama3.1:8b, deepseek-r1:8b, mistral (GPU-optimized, 100% private)
- Cloud Providers: Claude Sonnet 4.5, GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0, Mistral Large, Cohere Command R+
- Benchmarking: Side-by-side comparison with latency, cost, and quality metrics
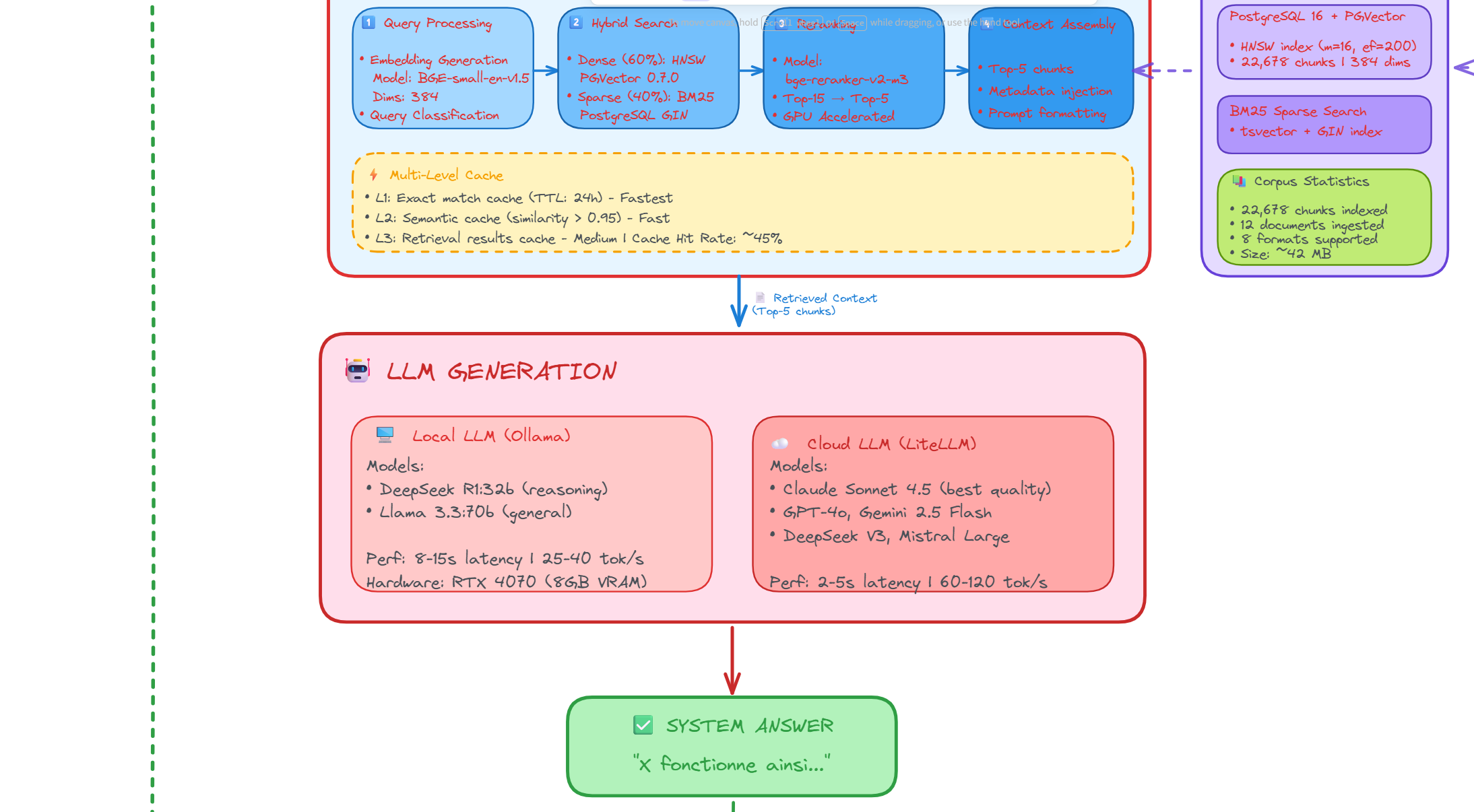
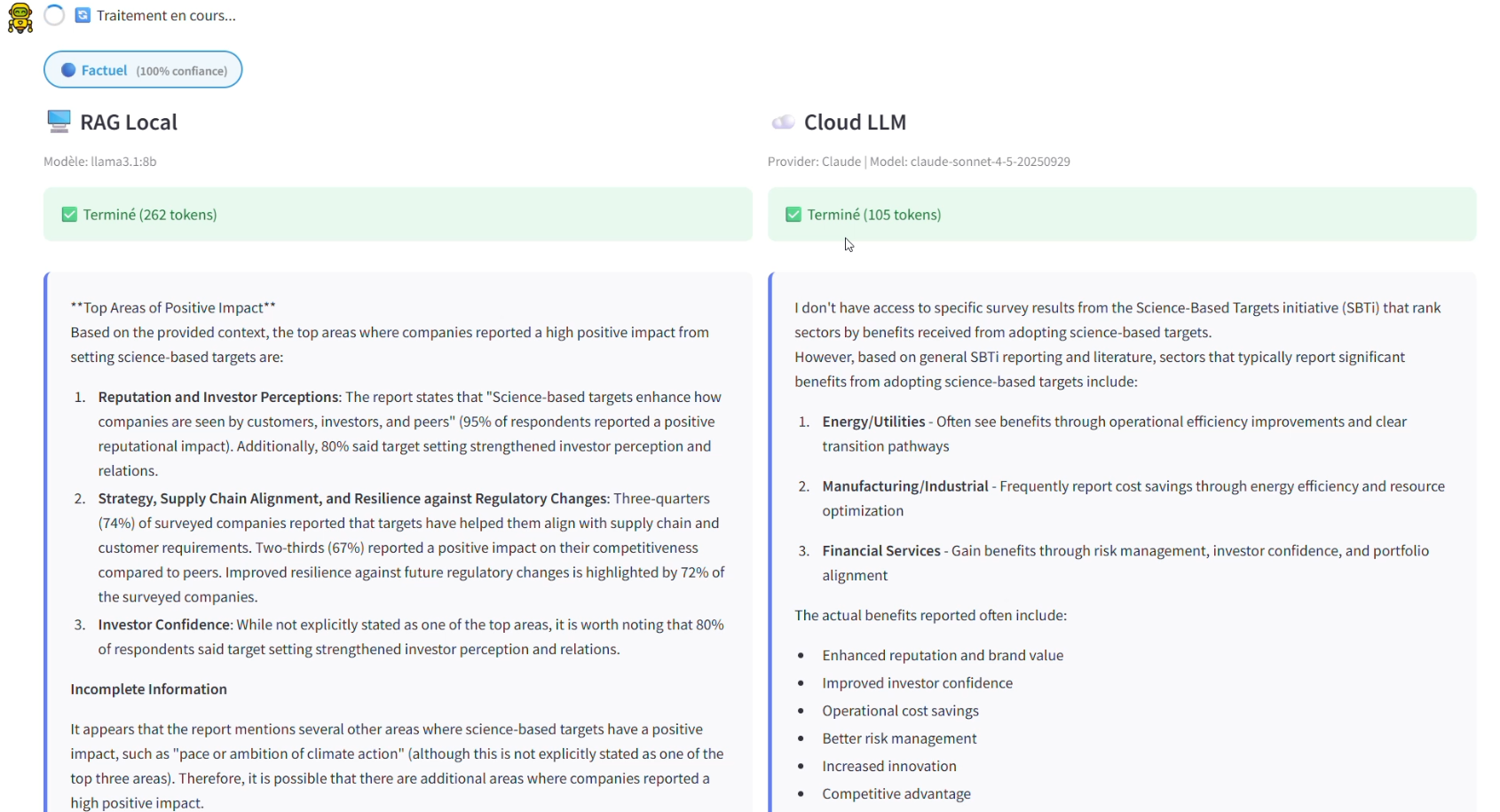
Figure 3 - Real-time comparison between local and cloud LLM responses
4. Automated Document Ingestion Pipeline
A production-grade ETL pipeline processes documents through parsing, chunking, quality filtering, and GPU-accelerated embedding generation.
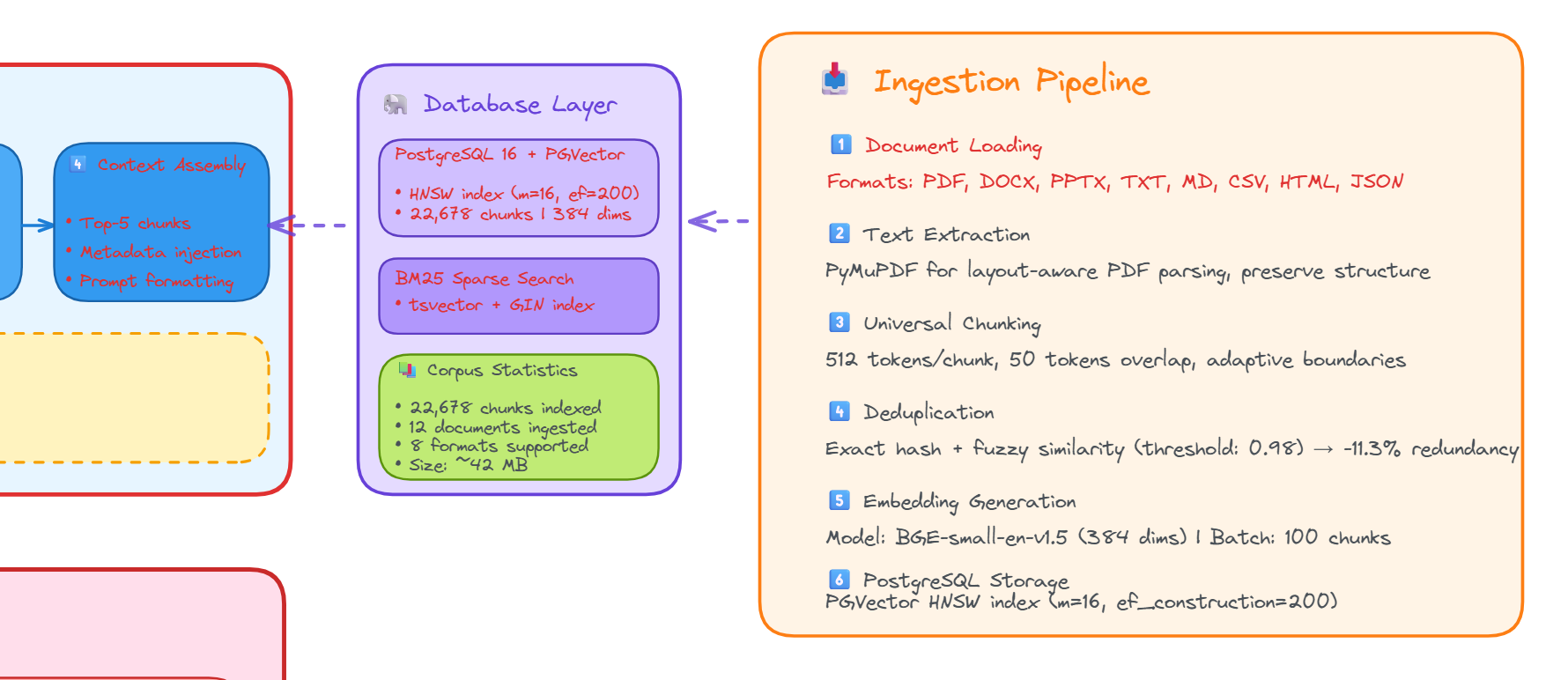
Figure 4 - Automated document ingestion pipeline architecture
- Format Support: PDF, DOCX, TXT, Markdown, code files, Jupyter notebooks
- Chunking: 512-1024 chars with semantic boundary detection and metadata preservation
- Quality Filtering: Language detection, deduplication, coherence scoring
- Storage: PostgreSQL/PGVector with HNSW indexing and full-text search
5. Technical Implementation
PostgreSQL 15+ with PGVector extension, Docker containerization, and Streamlit interface.
- Database: PGVector with HNSW indexing (m=32, ef_construction=128) and full-text search capabilities
- Framework: LangChain with multi-provider support (Ollama, Claude, GPT-4, Gemini, Mistral)
- ML/NLP: PyTorch, Sentence-Transformers, spaCy, CrossEncoder
- Infrastructure: Docker deployment with Streamlit UI and Python 3.9+
6. User Interface
Streamlit-based interface with chat interaction, source citations, side-by-side local/cloud comparison, and document upload capabilities.
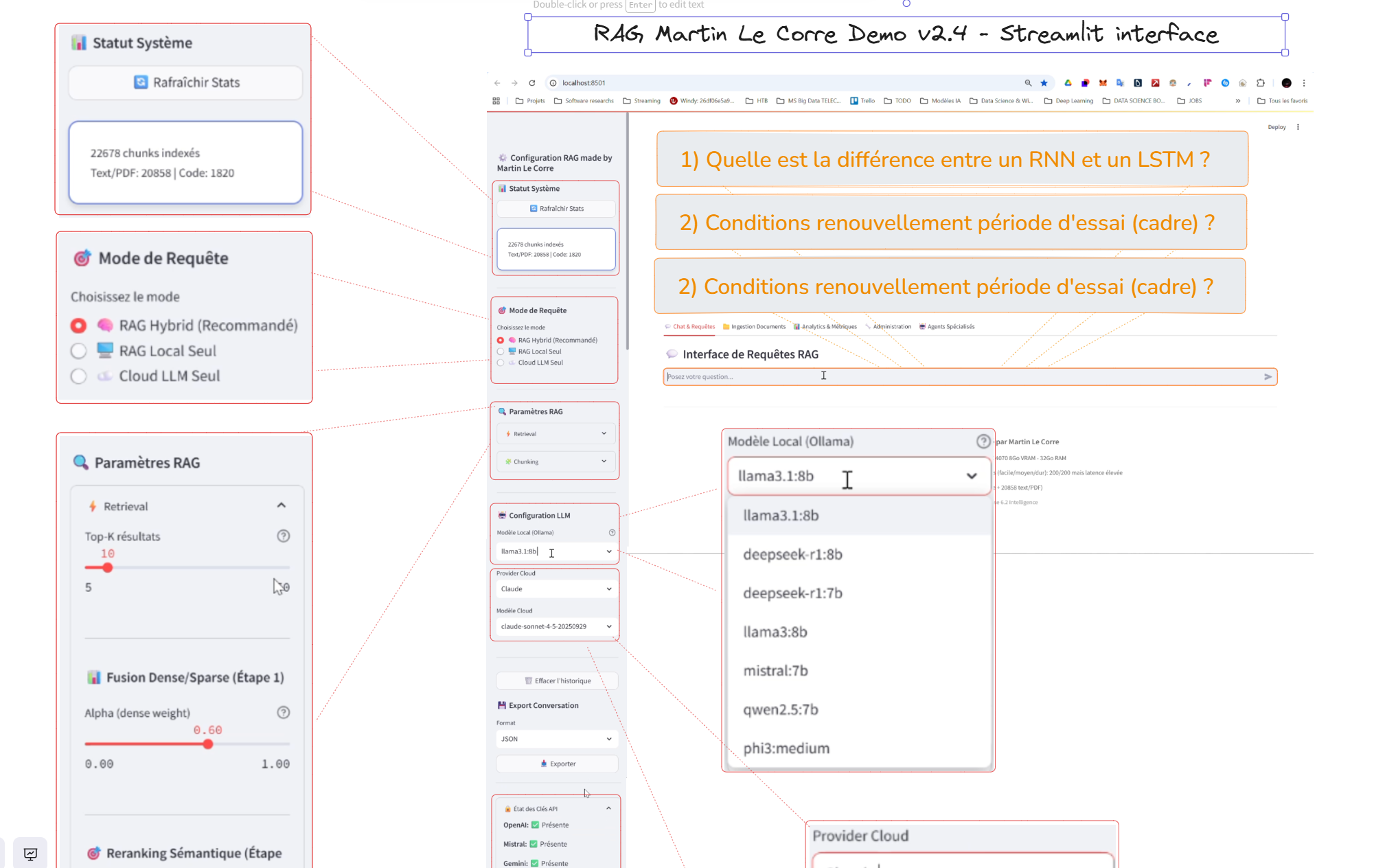
Figure 7 - Interactive Streamlit interface
8. Conclusion
This project demonstrates a production-ready RAG system combining 100% on-premise capability with multi-cloud flexibility. Hybrid retrieval (dense + sparse + RRF) delivers superior accuracy, while SQL-native fusion provides 10x performance gains over Python implementations.
Future enhancements include multi-agent integration, graph-based retrieval, multimodal support, and enterprise scalability for millions of chunks.
References & Resources
Key Technologies
- LangChain: Framework for developing applications powered by language models - https://python.langchain.com/
- PGVector: Open-source vector similarity search for PostgreSQL - https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector
- Ollama: Run large language models locally - https://ollama.ai/
- BAAI/bge-m3: Multilingual embedding model - https://huggingface.co/BAAI/bge-m3
- Sentence-Transformers: Python framework for state-of-the-art sentence and text embeddings - https://www.sbert.net/
Project Information
Status: Production-ready, fully deployable
Contact: For repository access or technical inquiries, contact Martin LE CORRE
Documentation: 📄 View detailed README